Contents
- 1 Understanding
- 2 What is an orphan account meaning?
- 3 Risks associated with orphan account meaning
- 4 Identifying Oorphan account meaning
- 5 Managing and Mitigating Risks orphan account meaning
- 6 Case Studies and Examples orphan account meaning
- 7 Best Practices for Organizations orphan account meaning
- 8 Conclusion
Understanding
Orphan account meaning In this digital age companies are becoming more dependent on different platforms and systems online to run their businesses. In this tangled web the concept of “orphan account” has gained much attention because of its security implications and integrity of data. This article will impart the reader with a thorough knowledge of orphan accounts, their associated risks, as well as strategies for managing them effectively.
What is an orphan account meaning?
An orphan account meaning is an account of a user that is active in a system, but is not able to be connected to an actual user. This usually occurs when an employee departs from an organization, or when a contractor has completed their contract or there is an error in the deactivation process. The accounts may be in a variety of forms, including email accounts, user accounts, access credentials to databases and many other.
Causes of orphan account meaning
A variety of factors can contribute to the creation of accounts with no owner:
employee turnover If employees leave the company and leave the company, their accounts will not be removed immediately.
Role changes Internal transfers and changes in roles can result in account creation, while the old ones remain in use.
Access to Vendors and Contractors Access granted temporarily to vendors or contractors can be converted into orphan accounts if they are not properly controlled and then deactivated after engagement.
mergers and acquisitions Integration of systems from various organizations could result in accounts being ignored.
The absence of Centralized Account Management: The lack of centralization in systems makes it difficult to manage and track users’ accounts definitely.
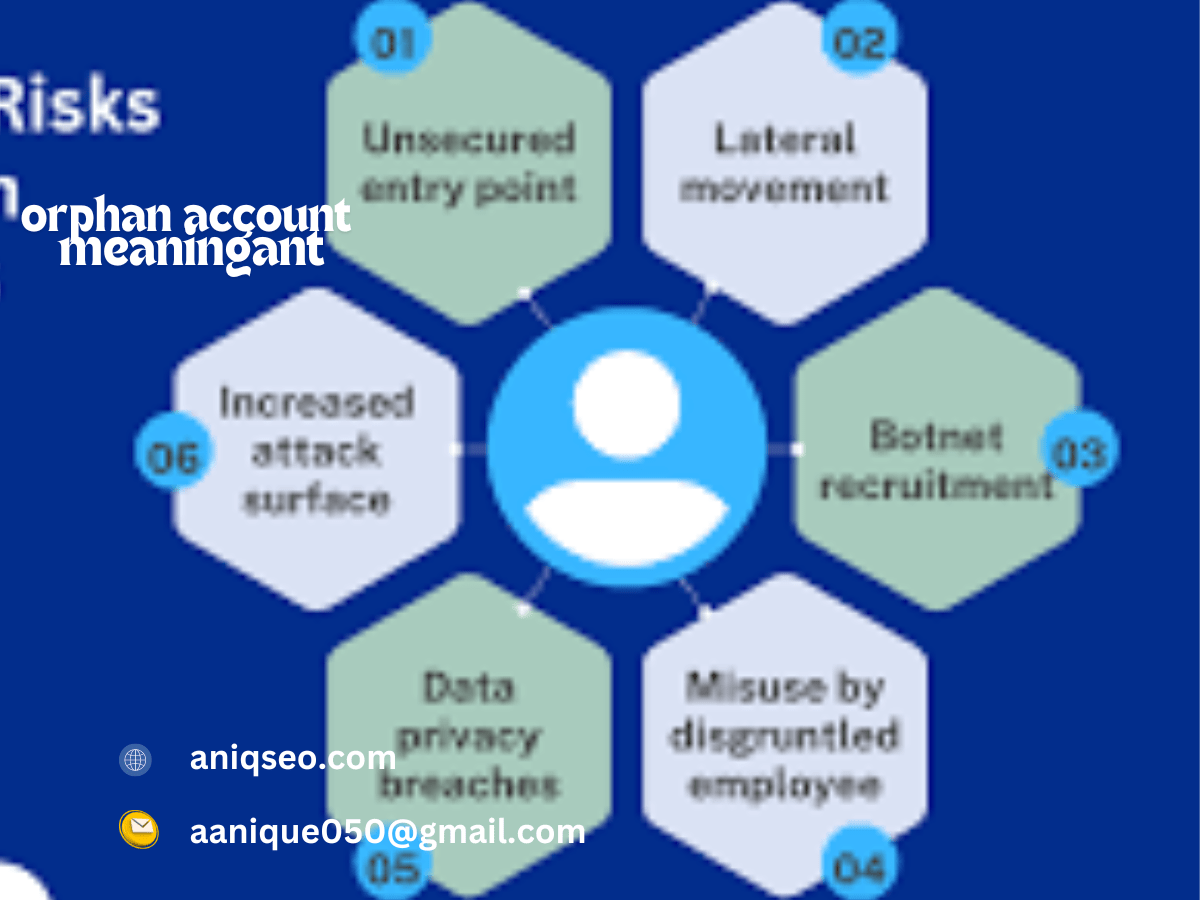
Risks associated with orphan account meaning
The risk of having a failed account is significant for organizations, such as:
Security Risks Accounts that aren’t monitored could be an entry point for cyberattacks. Hackers can make use of the accounts in order to collect unauthorised access to sensitive data.
Data Breach Active accounts that do not have an associated user could be used to smuggle data, resulting in potential data breach and issues with compliance.
Compliance Verses Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX have strict controls on the access of users. In the event of an account being abandoned, it can lead to the violation of regulations and huge fines.
Operations Inefficiencies Accounts with no owner can consume resources and license fees in excess, resulting in costs that are not worth it.
insider threats Former employees or contractors who have access residual can deliberately misuse orphan accounts.
Identifying Oorphan account meaning
Recognizing orphan accounts requires an extensive review of accounts used by users across every system. Important steps include:
regular audits Perform regular checks of user accounts in order to find any accounts that have been removed from active users.
automated tools Make use of Identity and Access Management (IAM) tools to automatically detect and flag invalid accounts.
Cross-Referencing Cross-refer HR records to systems accounts in order to warrant account are not disabled after an employee has left.
Behavior Monitoring Check the activity of your account for indications of unusual behavior. This could indicate that an account has been used in a fraudulent manner.
Managing and Mitigating Risks orphan account meaning
The effective management of accounts with orphans requires a variety of strategies:
Centralized Account Management: Establish central IAM systems that streamline creating, monitoring or deactivation of accounts for users.
Automated deactivation Automate the process for deactivation to instantly disable accounts after an employee quits the company.
Periodic Review Set up a timetable to conduct periodic checks of each user account in order to warrant that there aren’t any accounts that don’t exist.
Role-based Access Control (orphan account meaning): Implement RBAC to assure that users get access to resources that they require and minimizing the potential impact of orphan accounts.
Offboarding Methods Develop complete offboarding procedures, including immediate removal of user accounts as well as retrieval of assets belonging to the company.
Learning and Education educate employees on the importance of prompt account management as well as the dangers of orphan accounts.
Case Studies and Examples orphan account meaning
Case Study 1: The 2013 Target Data Breach
In 2013 Target was the victim of one of the biggest data breaches ever which affected over 40 million debit and credit card accounts. The incident was traced to stolen network credentials from an unidentified third-party vendor. This incident demonstrates the significant danger posed by poorly managed third-party accounts, which could turn into orphan accounts if they are not properly managed.
Case Study 2: Healthcare Provider’s Compliance Fine
A major healthcare company was penalized under orphan account meaning rules due to an information breach that involved accounts that were not registered. A thorough investigation revealed that a number of accounts belonging to former employees were active and patient data was obtained via the accounts. This highlights the need for strict deactivation of accounts to avoid fines from regulatory authorities.
Best Practices for Organizations orphan account meaning
To protect themselves from the risk that come with accounts that are not in use To reduce the risk of orphan accounts, businesses should adopt these excellent practices:
Install IAM Solutions: Invest in solid IAM solutions that provide automated management of accounts, which includes monitoring, creation and deactivation.
Create Comprehensive Policies Set up and enforce policies that are comprehensive and include procedures for the management of user accounts with clear guidelines for account cancellation.
regular training Regularly conduct session of training for IT employees along with other workers to warrant that they know the importance of having a good account management.
Check and review Conduct regular reviews and audits on all users’ accounts in order to assure that all accounts are in compliance with company policies and the regulatory requirements.
Third Party Management Control over access to third parties, which includes periodic reviews and the immediate deactivation of accounts if access to the account is not required.
Use Multi-Factor authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to add an additional layer of security for users’ accounts. This makes it difficult for users who are not authorized to use orphan accounts.
Conclusion
orphan account meaning Accounts that are not properly managed pose a serious risk to security and compliance for companies. Recognizing their root reasons, identifying weaknesses, and implementing effective management strategies are crucial actions to mitigate these risks. Through implementing excellent practices and using the latest IAM solutions, businesses have the ability to definitely handle user accounts and ensure that accounts with no parental rights are not a conduit to cyber-attacks and data security breaches. Regularly scheduled checks, automated deactivation procedures and thorough offboarding processes are essential to ensure the security and compliance of your digital environment.